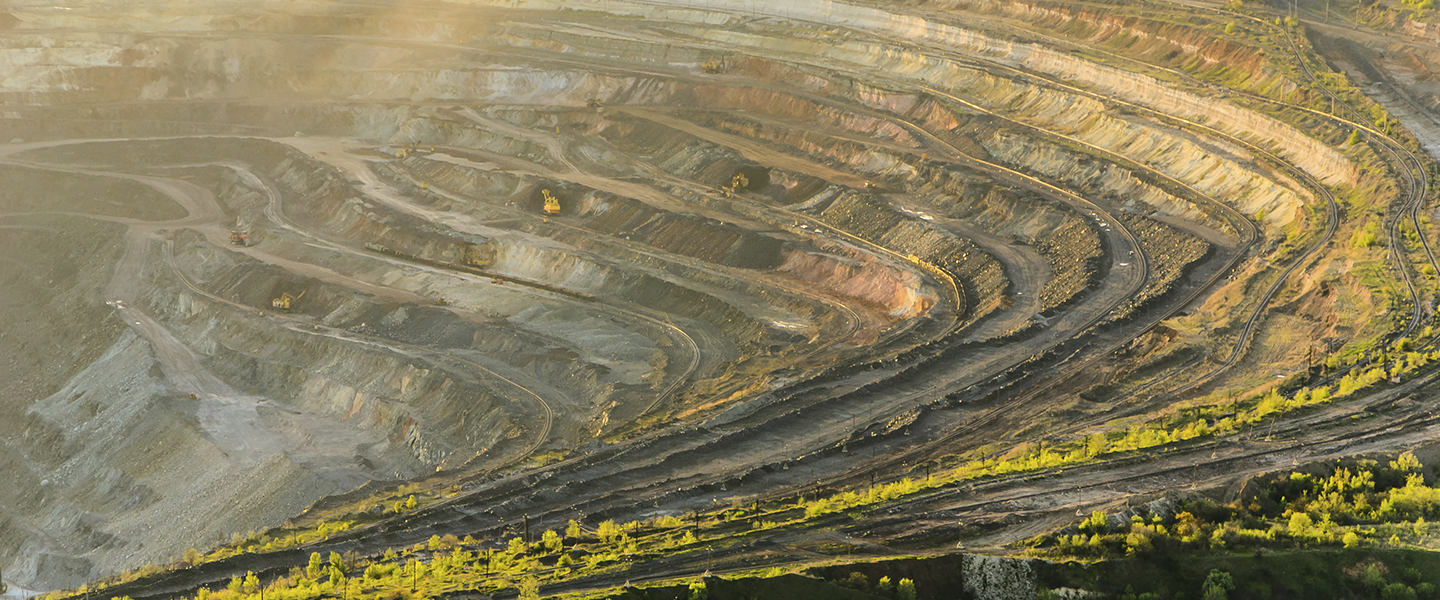
Nuestras Soluciones
Mejora la productividad, eficiencia y seguridad de tu mina usando el valor de tus datos. Proveemos soluciones de data analytics y simulación en minería que ayudan a tomar mejores decisiones en Planificación, Geotecnia, Excelencia Operacional y Operaciones Mina.
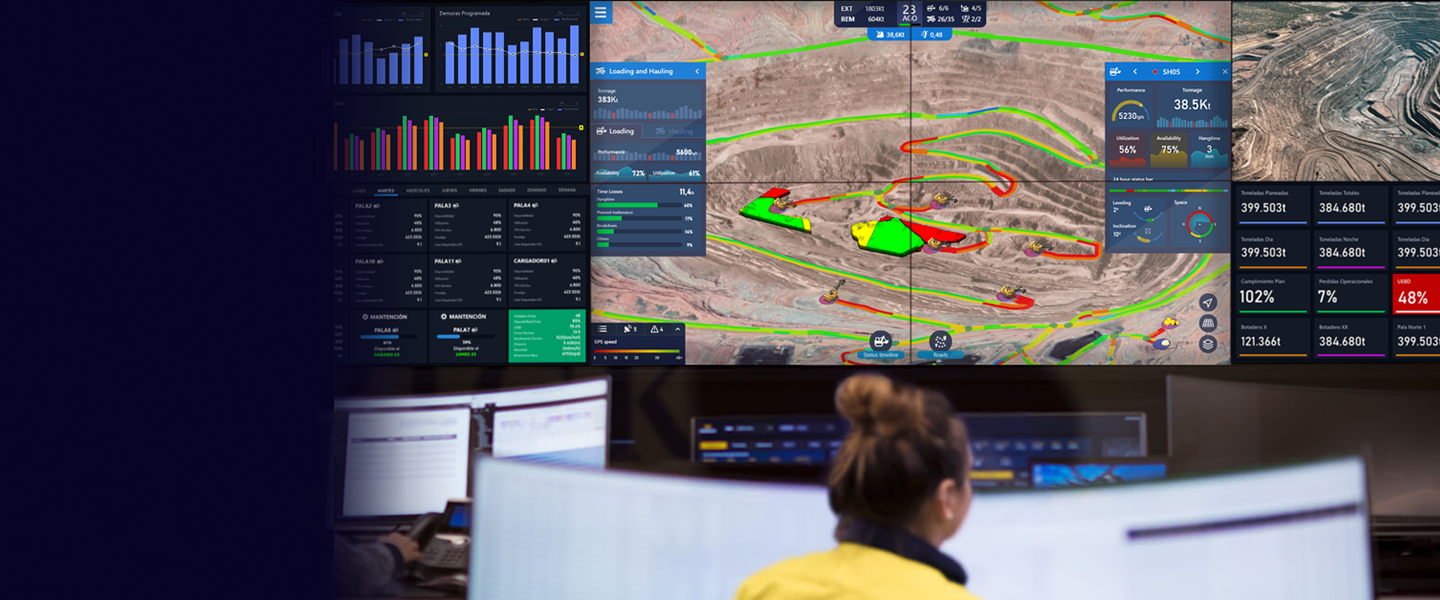
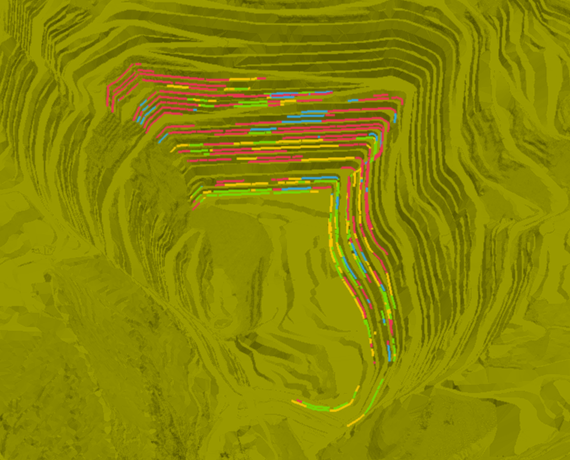
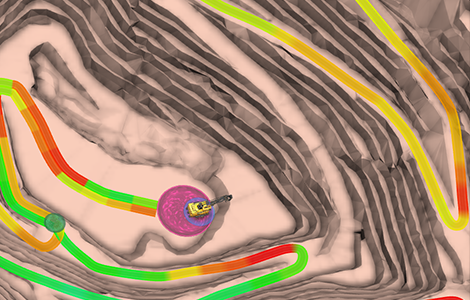
TIMining Aware
Aumenta el cumplimiento del plan y las velocidades promedio con el monitoreo de estos KPIs en tiempo real
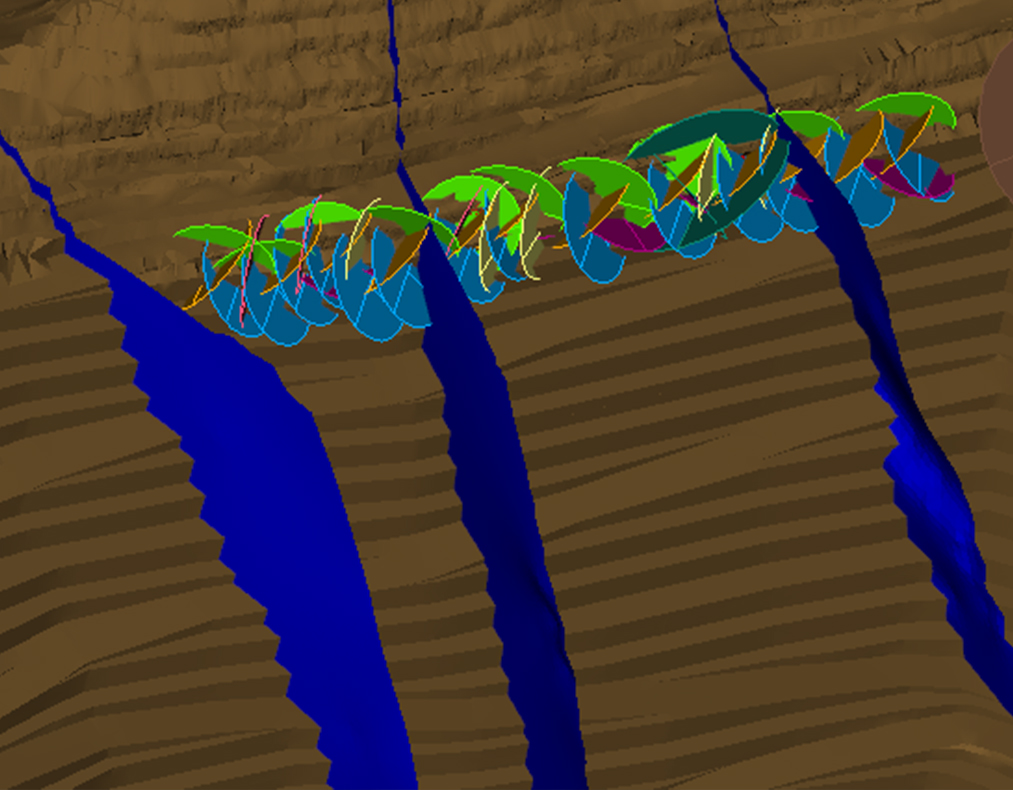
Drillit
Monitoreo del proceso de Perforación y Tronadura, QA/QC automático y conciliación de los planes de perforación.
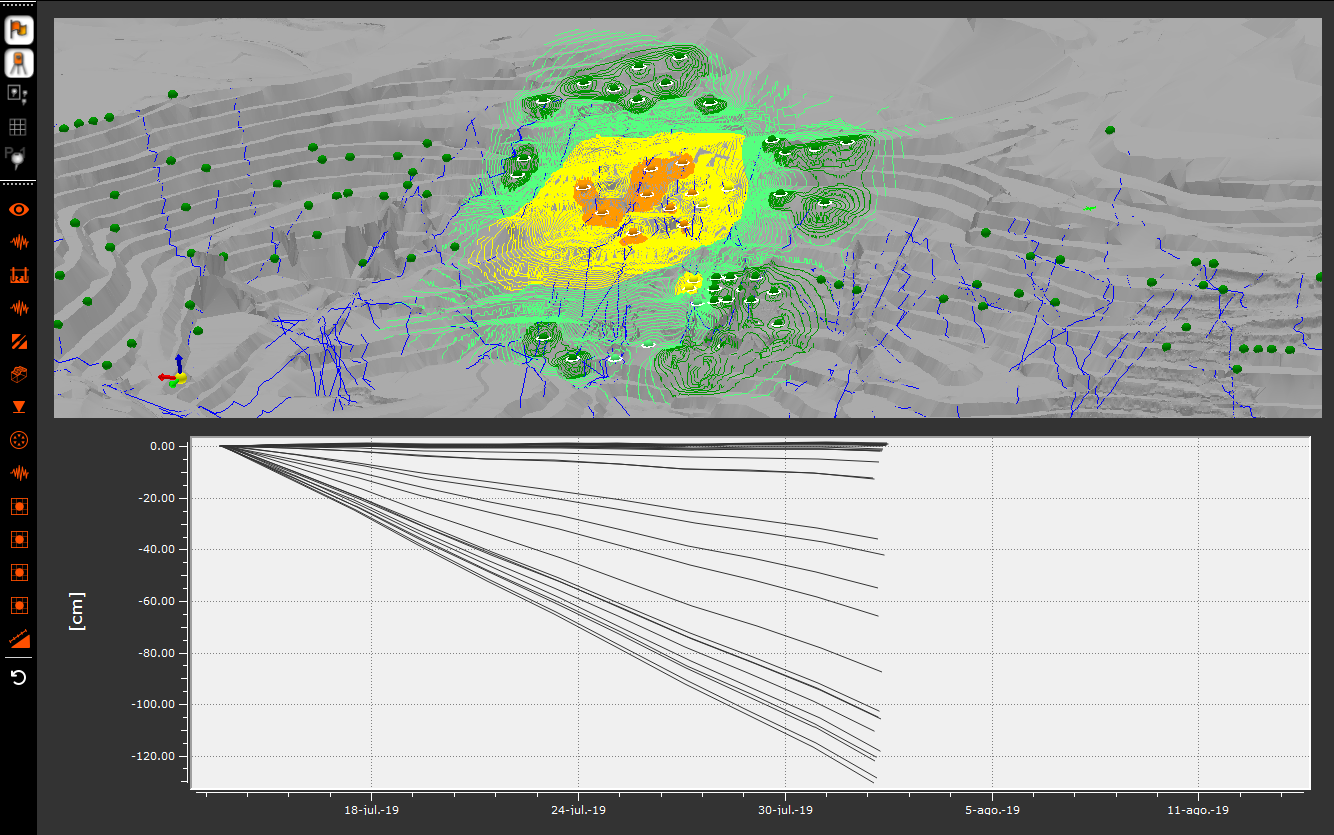
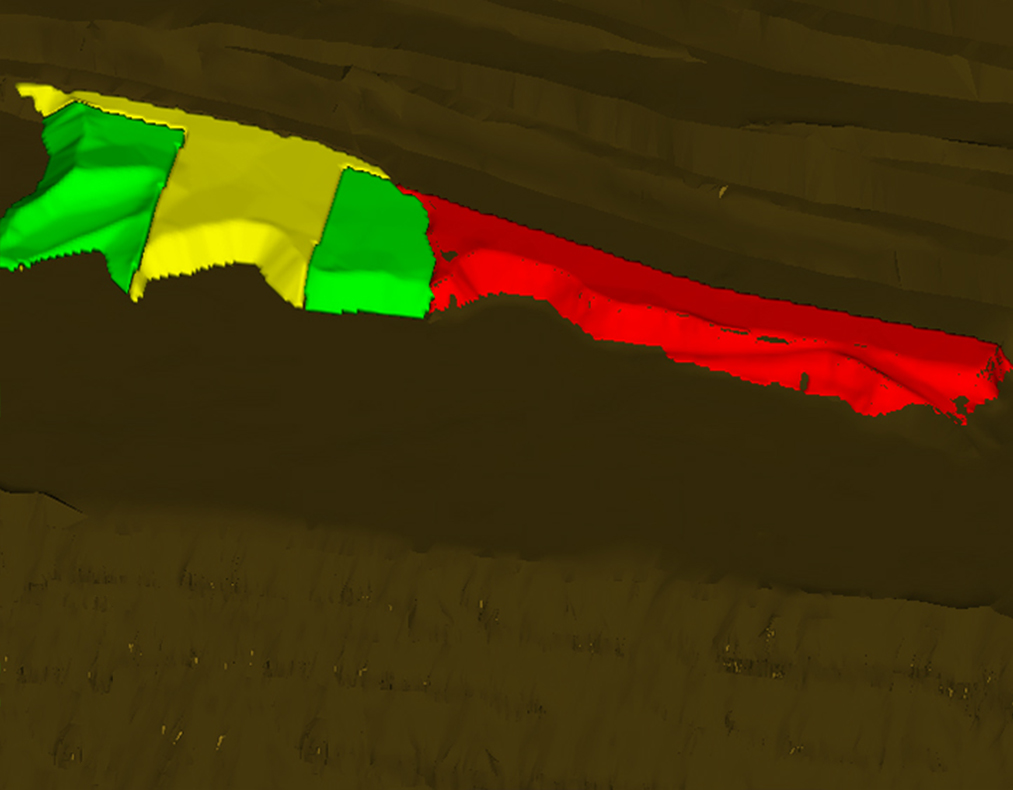
Aris
Integración de monitoreo y vigilancia geotécnica para rajos, botaderos, pilas y tranque
presencia
Somos una empresa de software para la minería, enfocada 100% en tecnología para la industria minera. Creamos soluciones para una minería más eficiente, productiva, segura y sustentable.
-
80
DISEÑADORES, INGENIEROS Y MINEROS
-
32
MINAS USANDO NUESTRAS SOLUCIONES
-
10
Años en el mercado minero global
-
8
PAISES CON PRESENCIA
tecnologías utilizadas

Minería 4.0
Minería 4.0 es la revolución tecnológica 4.0 aplicada a la minería, habilitada por las altas capacidades de análisis de datos, inteligencia artificial, simulación y conectividad. Estas tecnologías tienen crecimiento exponencial y pueden cambiar las industrias en las que impactan.
Digital Twins
Un Gemelo Digital o Digital Twin es un modelo digital de un proceso o activo físico que se construye desde datos de sensores y equipos. Los Gemelos Digitales permiten entender, predecir y optimizar el desempeño de procesos y sistemas.

Inteligencia A
umentada
Inteligencia aumentada es el uso de la tecnología para aumentar la inteligencia humana combinandola con procesamiento de inteligencia artificial, en vez de reemplazarla por inteligencia artificial.
Empresas que trabajan con nosotros.
Las mayores corporaciones del mundo operan sus minas con soluciones de software minero de TIMining. Acuerdos corporativos y aprobaciones de TI Corporativo hacen rápida y fácil la adquisición e implementación de soluciones de TIMining.